Statistics for Euthanasia in Canada
The deaths by euthanasia are shown by state.
Euthanasia in Canada
Euthanasia in Canada in its legal voluntary form is called Medical Assistance in Dying (MAID) and it first became legal along with assisted suicide in June 2016 for those whose death was reasonably foreseeable. Before this time, it was illegal as a form of culpable homicide. In March 2021, the law was further amended by Bill C-7 to include those suffering from a grievous and irremediable condition whose death was not reasonably foreseeable. The planned inclusion of people with mental illnesses is controversial and has been repeatedly delayed. The legality of this postponement to 2027 is being challenged in court.
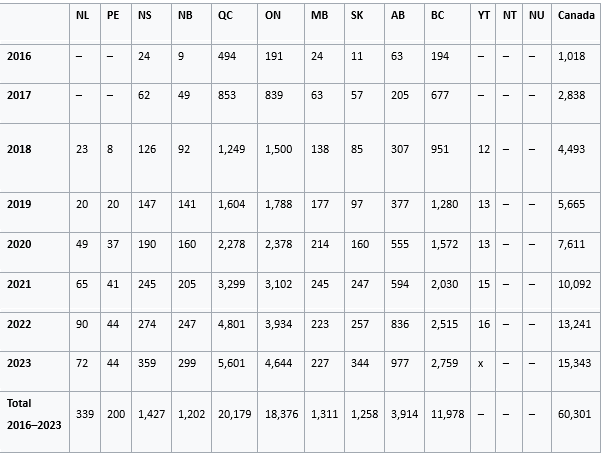
The intensity and breadth of Canada's MAID program has led to condemnation of its program by UN human rights experts and disability rights groups in Canada. It has also been the subject of substantial international attention and criticism. Human rights advocates have criticized Canada's euthanasia laws in a number of ways, including that it is lacking safeguards, devalues the lives of disabled people, prompts health workers and doctors to suggest euthanasia to people who would not otherwise consider it, or euthanizes people who were not receiving adequate government support to continue living. According to the Fifth Annual Report on MAID, there were 15,343 MAID provisions reported in Canada, accounting for 4.7% of all deaths in Canada. There have been 60,301 MAID deaths reported in Canada since the introduction of legislation in 2016.
Euthanasia was previously prohibited under the Criminal Code as a form of culpable homicide. The prohibition was overturned in a February 2015 decision by the Supreme Court of Canada in Carter v. Canada (Attorney General), which ruled that the Criminal Code provisions that make it a crime to help a person end their life violate the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms and that eligible adults with grievous and irremediable medical conditions are entitled to an assisted death. The Court delayed its suspension of invalidity for a period of 12 months, to allow Parliament the opportunity to amend its laws if it so chose. In January 2016, the Court granted an additional four-month extension to the suspension to allow for further time. As an interim measure, it ruled that provincial courts can now begin approving applications for euthanasia pursuant to the criteria in the Carter decision. On 6 June 2016, the suspension of invalidity expired, and the law was struck down. On 17 June 2016, a bill to legalize and regulate euthanasia passed in Canada's Parliament. Canada's current law makes euthanasia available only to residents eligible for Canadian healthcare coverage.
The previous law's requirement that a natural death must be reasonably foreseeable and that the medical condition be grievous and irremediable medical condition had been controversial for how it limited the original Supreme Court of Canada ruling, mandating that euthanasia be made available to all adults with grievous and irremediable medical conditions. The British Columbia Civil Liberties Association (BCCLA) challenged the constitutionality of the previous law because it excluded people with long-term disabilities and those with "curable" medical conditions whose only treatment options people may find unacceptable. The BCCLA argued these medical conditions should qualify under the court's definition of grievous and irremediable. The BC Supreme Court and the Quebec Supreme Court in Truchon ruled in 2019 that the law could not limit euthanasia only to individuals whose death was reasonably foreseeable. The current law prohibits mental illnesses as being considered as a grievous and irremediable condition. This prohibition was initially set to expire on 17 March 2023. On 2 February 2023, the Canadian government introduced legislation to extend the temporary exclusion of eligibility in circumstances where a person's sole underlying medical condition is a mental illness for a period of one-year, until 17 March 2024. In 2024, this was further delayed until 2027. After this date, persons with a mental illness can be eligible for medical assistance in dying, subject to any further amendments to the law or any new regulations. Canada's euthanasia law includes some legal safeguards aimed at preventing abuse and ensuring informed consent. Neither the legal witness nor the physicians involved can have any legal or financial interest in the outcomes of the patient. Consent must be repeatedly expressed, not implied, including in the moment right before death. Consent can be revoked at any time, in any manner. There are no consequences for backing out and there are no limits to how often it can be requested. Doctors are permitted to suggest euthanasia to patients, regardless of whether the patient has already said that they do not want it. To receive euthanasia, patients experiencing disease, disability or terminal illness must sign a written request expressing their wish to end their life in front of one independent witness who can confirm it was done willingly free of coercion. Next, two physicians and/or nurse practitioners must independently confirm their written agreement that the patient has an incurable grievous and irremediable medical condition that is in an advanced state of irreversible decline, and that the patient is capable of receiving and willing to receive euthanasia. If their death is not reasonably foreseeable, a medical expert in the underlying medical condition must sign off on the request, their assessment must take at least 90 days, and they must be informed about and decline all other forms of treatment, including palliative care. Canada's law is consistent with many other nations that allow euthanasia in requiring at least two physicians to confirm the details of a diagnosis. Canada's law no longer requires the presence of a terminal illness, unlike many other countries where euthanasia is only legal in those circumstances. Canada's law is more restrictive than those of Belgium and the Netherlands in that it does not permit minors access to euthanasia. Canada does not yet allow it on the grounds of mental illness, a practice allowed in the Netherlands, Belgium, and Switzerland, until at least 17 March 2027. Canada's law is less restrictive in that it does not require a patient to have exhausted all other treatment options, unlike Belgium and the Netherlands. While Belgium allows advanced directives in all circumstances, such advance directives in Canada may only be used if the patient's death is reasonably foreseeable. Canada is the only country that allows nurses to administer the drugs used for euthanasia. According to The Atlantic, "the law currently states that any sign of patient refusal of MAID under an advance directive 'must be respected'; at the same time, if the clinician determines that expressions of resistance are 'behavioural symptoms' of a patient's illness, and not necessarily an actual objection to receiving MAID, the euthanasia can continue anyway."
The federal government passed Bill C-7 on 17 March 2021. The new legislation distinguished two "tracks" for assisted death. Under Track 1, the legislation relaxed or eliminated some of the safeguards for patients whose deaths were reasonably foreseeable, notably removing the 10-day waiting period, requiring only a single independent witness, and removing the requirement to offer palliative care. The legislation also introduced a new avenue, Track 2, for those whose death was not reasonably foreseeable to access euthanasia—conditional on the approval of medical practitioner who specialized in the underlying condition; a 90-day assessment period; and ensuring "serious consideration" by applicants of "reasonable and available means" of treatment. The legislation included a sunset clause that would allow people with mental illnesses to be eligible for euthanasia two years after the legislation passed. This clause has been particularly controversial due to the perceived difficulty of receiving informed consent from individuals suffering from a mental illness, particularly when the mental illness is already associated with suicide ideation. However, multiple studies show that the majority of people with mental illnesses do not lack the mental competence or the capacity to make treatment-related decisions. This expansion in access to medical assistance in dying was originally planned for March 2023 before being postponed by one year, to 17 March 2024. It was further postponed to 2027.
A panel was established by the government to study potential issues and safeguards with implementing medical assistance in dying for people whose sole medical condition was a mental illness. A report of this process was given to parliament on 6 May 2022. The panel had nineteen recommendations that could be implemented without amending the Criminal Code. Some arguments addressed to the panel suggested that there was no evidence that safeguards and protocols could be adequate and thus the panel's mandate could not be fulfilled. The panel concluded that despite these uncertainties, people could still voluntarily wish to request medical assistance in dying and thus its mandate could be fulfilled. One member of the panel, Ellen Cohen, resigned for ethical reasons. Cohen believes that the issues faced by those in poverty or seeking housing was not adequately considered by the rest of the panel. A person can simultaneously seek medical assistance in dying while waiting for other treatments. Proponents of including mentally ill patients regard the delays as discriminatory. Opponents are sceptical that mental illness is irremediable or concerned about endangering vulnerable individuals. In 2024, a lawsuit about the legality of delaying expansion of euthanasia to those with a mental disorder was filed due to the belief that denying it on these grounds is discriminatory and violates the Charter of Rights and Freedoms. A separate charter challenge was also filed in 2024, on the grounds that the Track 2 criteria cause premature deaths of disabled people and euthanasia should be limited to those with reasonably foreseeable deaths.
There have been 60,301 MAID deaths reported in Canada since the introduction of legislation in 2016. In 2023, 15,343 MAID provisions were reported in Canada, accounting for 4.7% of all deaths in Canada. This represents a growth rate of 15.8% over 2022. The average age of individuals at the time MAID was provided in 2023 was 77.6 years. In 2022, the underlying medical conditions included cancer (63%), cardiovascular (18.8%), other at 14.9% (can be frailty, diabetes, chronic pain, autoimmune), respiratory (13.2%), and neurological conditions (12.6%). 75% of MAID recipients received palliative care and of the MAID recipients who required, but did not receive, palliative care 80.5% had access, a level similar to the three previous years.
Before euthanasia was made
legal in Quebec in June 2014, the Quebec College of Physicians had
declared that it was prepared to cross the line on the debate over euthanasia
and proposed that it be included as part of the appropriate care in certain
particular circumstances. The Canadian Medical Association (CMA)
describes euthanasia as "one of the most complex and ethically challenging
issues facing Canadian physicians". Before the legalization of
euthanasia, the organization stated that it is not up to them to decide on the
issue of euthanasia, but the responsibility of society. The organization also
reported that not all doctors were willing to help a terminally ill patient
die. A 2015 survey indicated that 29% of Canadian doctors surveyed would
consider providing euthanasia while 63% would refuse. However, the belief
in late 2015 was that no physician would be forced to do so. The extent of
conscientious objection to providing euthanasia continues to be debated on
issues such as whether objecting physicians must refer patients to a doctor who
is willing to provide euthanasia and whether institutions have a right to refuse
to provide euthanasia services; at present doctors are required to make
effective referrals. Catholic hospitals often refuse to provide
healthcare that goes against the institution's tenets, such as abortion or
euthanasia. A 2023 survey by the Angus Reid Institute showed 61% of Canadians
supported the current version of the legislation, while 31% supported extending
euthanasia to mental disorders. A poll conducted by Leger in the summer
of 2022 regarding further liberalization of Canada's euthanasia laws found that
51% of Canadians supported expanding euthanasia to mature minors, with 23%
opposed and 26% being unsure. 65% supported advanced directives in the face of
a worsening cognitive condition, with 14% opposed and 22% being unsure. 45%
supported expanding eligibility for euthanasia to include individuals with
serious mental illnesses, with 23% opposed and 32% being unsure of their position.
In 2021, the United Nations Human Rights Council's special rapporteur on the rights of persons with disabilities criticized Bill C-7 and assisted death in general, for undermining both disabled people's equal right to live and their ability to autonomously access support to continue living. In 2025, a UN report recommended disqualifying non-terminal patients from being eligible for euthanasia. An estimated 25% of disabled Canadian adults live in poverty. In an August 2023 paper, Medical Assistance in Dying, Palliative Care, Safety, and Structural Vulnerability, the authors argued that while socioeconomic deprivation drives mortality to a large degree, it does not drive medical assistance in dying to any substantial degree. Another 2023 paper, The Realities of Medical Assistance in Dying in Canada, concluded that "The Canadian MAID regime is lacking the safeguards, data collection, and oversight necessary to protect Canadians against premature death." In certain cases, family members are not informed that their relative has died through MAID, as individuals have a right to medical privacy. While standard reviews of MAID cases may be conducted, Canada's process has been criticized for lacking regional panels and oversight processes that other countries with legal euthanasia provide.
After the repeal of the reasonably foreseeable requirement in Bill C-7, writers for The Spectator, Jacobin, and Global News have argued that many might opt into euthanasia because of poverty. Critics believe that a lack of social spending structurally places these people in poverty, and then introduces MAID as a way out, citing issues like insufficient welfare for disabled people and unconstitutionally long waiting times for healthcare as evidence that those who are disabled and impoverished do not have enough support to survive. An analysis piece from The Spectator, their most popular article in 2022, stated that the Canadian government sees MAID as a more economical alternative to investments in social programs and welfare. The Canadian Parliamentary Budget Officer released a report claiming the old MAID policies will save Canada $86.9 million per year and that Bill C-7 will save an additional $62 million per year. There have also been intersectional issues raised with MAID relating to higher rates of poverty in marginalized communities, lack of social support, and ableism and racism in the medical community.
In addition to broader criticism of MAID, the handling of certain cases has been subject to media coverage. These include:
- In 2017, a mother of a young woman with cerebral palsy was told by a doctor that not applying for MAID was "selfish". Her daughter was in the room when the conversation took place and described the experience as traumatic.
- In 2018, Roger Foley was being treated for cerebellar ataxia at an Ontario hospital. Foley alleged that his only options were to be forcibly discharged from the hospital and then treated by an organization that had previously failed to provide him adequate care or apply for MAID. Foley hired a lawyer for a charter challenge. In 2024, his lawsuit against this hospital was dismissed with the presiding judge noting "It makes very serious allegations in the form of bare conclusions, without pleading material facts to support those allegations" as well as "These submissions were irrelevant and ... also betray the fundamentally political nature of many of Mr. Foley's complaints."
- In 2019, Alan Nichols successfully applied for MAID while being hospitalized for suicide ideation in Chilliwack, B.C. He was euthanised, despite concerns being raised to the nurse practitioner by his relatives. The reason given on his application form requesting euthanasia was only 'hearing loss'.
- In September 2021, Rosina Kamis, a 41-year-old Malaysian-born woman, applied for MAID citing fibromyalgia as the reason. However, in conversations and recordings shared with friends, she mentioned financial hardship and social isolation as additional factors influencing her decision.
- In February 2022, an anonymous Torontonian suffering from extreme chemical sensitivity syndrome with the pseudonym Sophia had a medically assisted death after failing to find affordable housing that was free from tobacco smoke and other chemicals. This case was addressed by her health care provider in testimony provided to the Special Joint Committee on MAID, and was referenced in their final report.
- In October 2022, a man from St. Catharines applied for MAID when facing homelessness. After receiving $60,000 from a GoFundMe campaign, he was able to find a place to live and withdrew his application.
- In November 2022, an anonymous active Canadian Forces member has alleged he was offered MAID when seeking assistance regarding PTSD and suicidal thoughts.
- In December 2022, Paralympian and veteran Christine Gauthier testified that a Veterans Affairs Canada employee offered her MAID as an option when she was fighting for the installation of a wheelchair lift or ramp at her house. Subsequently, VAC claimed they found no record that MAID was offered as an option to Gauthier and that it found four such cases, all involving a single now-suspended case manager.
- In August 2022, Vancouver Coastal Health asked patients seeking mental healthcare for suicidal ideation if they would like to consider MAID, which the patients experienced as undermining their access to suicide prevention care; the hospital stated the suggestion was a method of assessing suicide risk.
- In February 2024, a 27-year-old woman with autism was scheduled for euthanasia in Alberta. Her father sought a temporary injunction through the justice system to prevent her death. The injunction was initially granted, but the father later dropped his appeal.